Cancers
in Women
Images do not represent real patients
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease, in which abnormal cells grow out of control and can spread to other parts of the body. It can start in almost any organ or tissue. Cancer that spreads from where it started to other parts of the body, is called metastatic cancer.1
Cancer may also be referred to as a malignant tumour, or neoplasm.1
Cancers that affect women
Some of the most common cancers in women are breast, cervical and endometrial cancer.2
Cancers that start in the female reproductive organs are called gynaecological cancers.3
In South Africa, breast and cervical cancer are the top two cancers affecting women.4
Living with Cancer
Living with cancer can be challenging, both physically and emotionally, but you do not have to go through it alone:6
- Reach out to support groups, such as CANSA, Wings of Hope, Cancer Alliance, for guidance and encouragement
- Take a trusted friend or family member to appointments. They can take notes, ask questions and remind you to mention symptoms or side effects
- Become familiar with your healthcare team — your oncologist, nurse, pharmacist and other Health Care Professionals. Ask who to contact for different concerns, whether about treatment, side effects, or emotional support
- After treatment, you will have regular follow-up visits — use these visits to discuss challenges you may face ahead. Knowing what to expect may help you make plans, as you find a “new normal” with cancer as part of your life

Committed to Care
MSD is committed to finding new treatments that could help people with cancer live better lives. Clinical trials for gynaecological cancers, test new treatments to see if they can help prevent, detect, or treat cancer.5
Which women’s cancer would you like to learn more about?

Triple-Negative Breast Cancer is a type of breast cancer that does not have certain hormone or protein receptors on the cancer cells.7

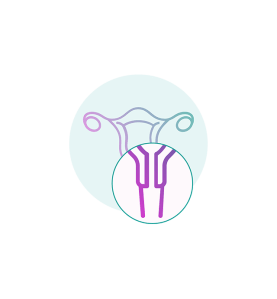
Cervical cancer is when abnormal cells in the lining of the cervix (part of the female reproductive system), grow in an uncontrolled way.3

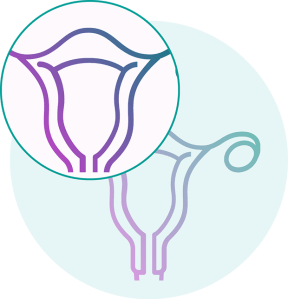
Endometrial cancer occurs when cells in the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus), begin to grow out of control.8

Images do not represent real patients
Commonly used cancer-related terms9-12
Biomarker
Features of a cancer that can help guide your treatment. Many biomarkers are mutations (changes) in the DNA of cancer cells.
Biopsy
A procedure that removes fluid or tissue samples, to be tested for a disease.
Brachytherapy
A type of radiation therapy in which radioactive material sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters, is placed directly into or near a tumour – also called internal radiation therapy.
Cancer
A group of diseases in which cells in the body change and grow out of control. Most types of cancer cells form a lump, or mass called a tumor. Not all tumors are cancer.
Cancer Grade
A rating of how abnormal cancer cells look, when viewed under a microscope.
Cancer Stage
A rating of the outlook of a cancer, based on its growth and spread.
Cervix
The lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina (birth canal).
Cone biopsy
A procedure, in which a cone-shaped piece of abnormal tissue is removed from the cervix. It may be used to gather more information about the extent of a cancer, or to treat some early cervical cancers. It is also called cervical conisation.
Ectocervix
The rounded, outer part of the cervix that extends into the vagina. The ectocervix is lined with cells, called squamous cells.
Endocervix
The inner part of the cervix that forms a canal between the vagina and the uterus. The endocervix is lined with columnar (glandular) cells that make mucus.
Endocrine therapy
A cancer treatment that stops the making or action of hormones, such as estrogen – also called hormone therapy.
Endometrium
The layer of tissue that lines the uterus.
Estrogen Receptor (ER)
A protein inside cells that binds to estrogen.
Estrogen Receptor-negative (ER-)
A type of breast cancer that does not use estrogen to grow.
Fallopian Tube
A thin tube, through which an egg travels from the ovary to the uterus.
Hormone
A chemical in the body that triggers a response from cells or organs.
Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor2 (HER2)
A protein on the surface of a cell that sends signals for the cell to grow.
Lymph
Clear fluid that flows through the lymphatic vessels throughout the body.
Lymph node
Small bean-shaped collection of immune system tissue, such as lymphocytes, found throughout the body along lymphatic vessels. They remove cell waste, germs, and other harmful substances from lymph. They help fight infections and also have a role in fighting cancer, although cancers can spread through them. Sometimes called lymph glands.
Malignant
A cancerous tumour that is dangerous or likely to cause death if untreated.
Mammogram
A picture of the insides of the breast that is created using x-rays.
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from the first tumour to another body part.
Mutation
Abnormal changes in a gene (pieces of DNA) that tell cells what to do and when to grow and divide). Most mutations do not cause cancer, but all types of cancer are thought to be due to gene mutations.
Neoplasm
An abnormal growth (tumor) that may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
Such a growth may be described as a neoplastic tumor.
Ovary
One of a pair of female reproductive organs that make hormones and eggs for reproduction.
Pathologist
A doctor who is an expert in testing cells and tissue to find disease.
Pelvis
The area of the body between the hip bones.
Precancerous
Changes in cells that may, but do not always, become cancer.
Progesterone Receptor (PR)
A protein inside cells that binds to progesterone.
Radiation Therapy (RT)
A treatment that uses high-energy rays – also called radiotherapy.
Recurrence
The return of cancer after treatment – also called a relapse.
Risk Factor
Something that increases the risk of developing a disease.
Screening
Tests, examinations, or procedures used to find cancer in people who have no symptoms. Screening increases the chances of finding certain cancers early, when they are small, have not spread, and might be easier to treat. This is different from diagnostic testing which focuses on trying to find out the cause of a person’s symptoms.
Side Effect
An unhealthy, or unpleasant physical or emotional response to treatment.
Systemic Therapy
Medicines that work throughout the body.
Targeted Therapy
Treatment with medicines that target a specific, or unique feature of cancer cells.
Transformation zone
The area where the endocervix and ectocervix meet. Most cervical cancers and pre-cancers start in the transformation zone.
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
A breast cancer that does not use hormones or the HER2 protein to grow.
Uterus
The organ where a foetus grows and develops during pregnancy – also called the womb.
References: 1. World Health Organization. Cancer. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer#tab=tab_1. Accessed 24 September 2025. 2. American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts for Women. 5 May 2025. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/understanding-cancer-risk/cancer-facts/cancer-facts-for-women.html. Accessed 24 September 2025. 3. Cancer Research UK. Women’s cancer (gynaecological cancer). 19 November 2024. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/womens-cancer. Accessed 24 September 2025. 4. The Cancer Association of South Africa. Cancer Statistics. Available from: https://cansa.org.za/south-african-cancer-statistics/. Accessed 24 September 2025. 5. MSD. Investigational Clinical Trials for Gynecologic Cancer. Available from: https://www.msdclinicaltrials.com/oncology/gynecologic/?page=1&lang=en. Accessed 24 September 2025. 6. Medline Plus. Cancer. Living with Cancer. 24 March 2025. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/cancerlivingwithcancer.html#. 7. Cancer Research UK. Triple Negative breast cancer. 24 September 2023. Available from: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/breast-cancer/types/triple-negative-breast-cancer. Accessed 24 September 2025. 8. American Cancer Society. What is endometrial cancer? 28 February 2025. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/endometrial-cancer/about/what-is-endometrial-cancer.html. Accessed 24 September 2025. 9. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Cervical Cancer. 2025. 10. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Invasive Breast Cancer. 2025. 11. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Uterine Cancer. 2023. 12. American Cancer Society. Cancer Glossary: Definitions & Phonetic Pronunciations. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/understanding-cancer/glossary.html. Accessed 24 September 2025.
ZA-NON-01074. Expiry date: 30/09/2027.
